Curtain Walls
In the realm of modern architecture, curtain walls have emerged as a revolutionary design feature. These versatile structures not only enhance the aesthetic appeal of buildings but also offer numerous functional advantages. This article explores the concept of curtain walls, their benefits, and their impact on contemporary architectural practices.
UNq DOORS
Revolutionizing Modern Architecture
A curtain wall refers to an external building envelope made of lightweight materials, such as glass, metal, or stone, that are hung from the building’s structural frame. Unlike traditional load-bearing walls, curtain walls do not support the weight of the building. Instead, they act as an aesthetic covering, offering protection from the elements while allowing natural light to penetrate the interior spaces.
Curtain walls have a rich history that dates back to ancient times. However, their modern development can be traced to the mid-19th century when advancements in glass manufacturing techniques enabled the creation of larger and more transparent facades. Over the years, the introduction of new materials, such as aluminum and steel, and advancements in structural engineering have revolutionized the design and functionality of curtain walls.
Advantages of Curtain Walls
Curtain walls offer several advantages that have made them popular in contemporary architecture:
Aesthetic Appeal:
Curtain walls provide a sleek and modern appearance, allowing architects to create visually striking buildings.
Natural Light: The extensive use of glass in curtain walls allows ample natural light to enter the building, reducing the need for artificial lighting and creating a pleasant indoor environment.
Energy Efficiency:
Advanced insulation techniques and the integration of energy-efficient glazing systems in curtain walls contribute to reduced energy consumption and lower heating and cooling costs.
Sound Insulation:
High-quality curtain walls can effectively minimize external noise, providing occupants with a quieter and more comfortable living or working environment.
Weather Protection:
Curtain walls act as a barrier against rain, wind, and other environmental elements, ensuring the building’s interior remains dry and secure.
Types of Curtain Walls
There are various types of curtain walls commonly used in architectural design. These include:
Stick System
The stick system is a traditional method of constructing curtain walls on-site, where individual components are assembled piece by piece. This approach offers flexibility in design and is suitable for projects with unique requirements.
Unitized System
The unitized system involves prefabricating curtain wall panels in a factory-controlled environment before transporting them to the construction site. This method offers faster installation, improved quality control, and reduced on-site labor.
Spandrel Panels
Spandrel panels are opaque or semi-opaque sections of a curtain wall that conceal structural elements, services, or floor slabs. They enhance the visual appearance of the building and provide thermal insulation.
Structural Glazing
Structural glazing utilizes specialized adhesives to bond glass panels directly to the supporting structure, eliminating the need for visible framing elements. This technique creates a seamless and transparent facade.
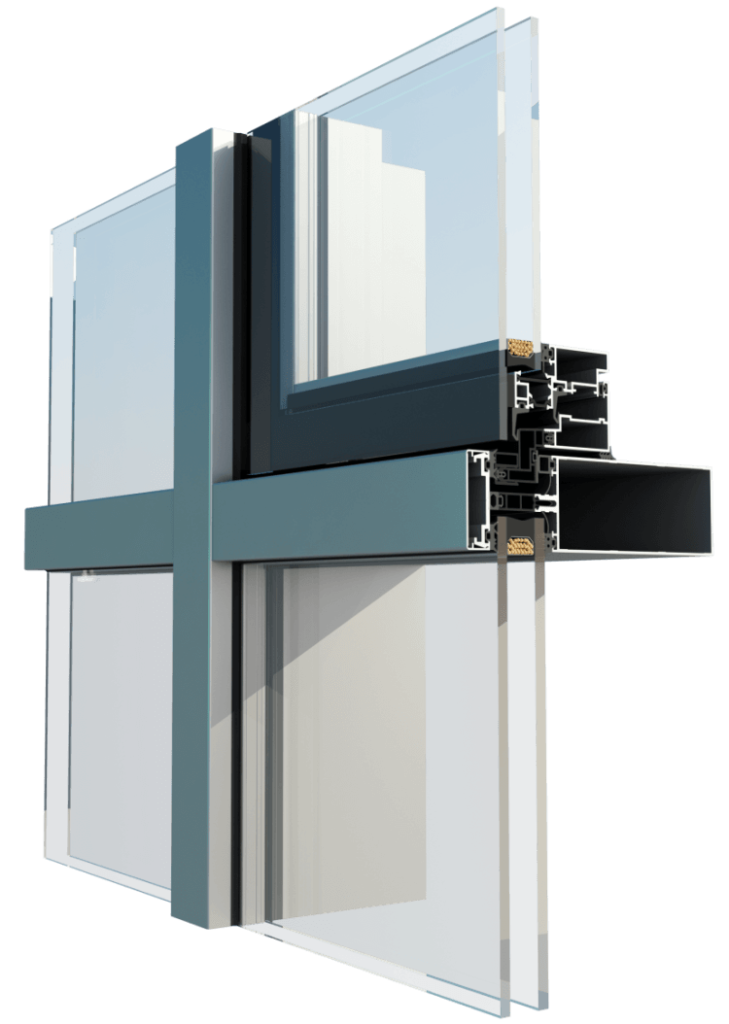
Understanding Curtain Wall Systems
Frame
The frame forms the structural backbone of the curtain wall system. It is typically made of lightweight, durable materials such as aluminum or steel. The frame provides support for the glass panels and other components, ensuring the stability and integrity of the structure.
Glass Panels
The most prominent feature of curtain walls, enabling the penetration of natural light and offering breathtaking views. Advanced glass technologies, such as double glazing and low-emissivity coatings, enhance insulation and reduce energy consumption.
Spandrel Panels
Spandrel panels are opaque panels located between the glass panels of a curtain wall. They conceal building components like HVAC systems, wiring, and plumbing, creating a seamless appearance.

Design Considerations for Curtain Walls
When incorporating curtain walls into architectural designs, several key factors must be taken into account:
Material Selection
The choice of materials for curtain walls depends on factors such as structural requirements, energy efficiency, and aesthetic preferences. Common materials include glass, aluminum, steel, and composite panels.
Energy Efficiency
Energy-efficient curtain walls employ double or triple glazing, low-emissivity coatings, and insulated frames to reduce heat transfer, thereby enhancing the building’s overall energy performance.
Acoustic Performance
To ensure acoustic comfort within the building, curtain walls can be designed with sound insulation properties, minimizing noise pollution from the external environment.
Maintenance and Durability
Regular maintenance is essential to preserve the longevity and performance of curtain walls. The selection of durable materials and the implementation of appropriate maintenance strategies contribute to the long-term reliability of the system.
Integration with Building Systems
Successful integration of curtain walls with other building systems, such as HVAC and lighting, is crucial to optimize energy efficiency, occupant comfort, and overall building performance.

Applications of Curtain Walls
Curtain walls can contribute to sustainable architecture by incorporating environmentally friendly features. These include the use of recyclable materials, energy-efficient glazing, and designs that promote natural ventilation and daylighting.
Curtain walls find extensive applications in various building types, including:
Commercial Buildings
Curtain walls are commonly used in commercial structures, such as office buildings, shopping malls, and hotels. Their transparency and modern aesthetics create an inviting and dynamic visual impact.
Residential Buildings
In residential construction, curtain walls are often employed in luxury apartments or penthouses, where panoramic views and abundant natural light are highly desirable.
Institutional Buildings
Educational institutions, hospitals, and government buildings often incorporate curtain walls to create a welcoming and visually appealing environment for occupants.
Cultural and Recreational Facilities
Museums, theaters, and sports stadiums utilize curtain walls to showcase architectural excellence, enhance visitor experience, and create an interplay between the built environment and surrounding landscapes.

Modern Architectural Design
Combines Aesthetics
Natural Lighting
Designing Buildings
Contact Us